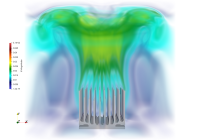
Grzegorz Gruszczyński, Application of the Lattice Boltzmann Method to conjugate heat transfer problems.
Abstract:
The Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM) has proved to be a very successful
numerical method for solving computational fluid dynamics problems.
Mainly due to the parallel performance it can achieve.
Knowing the limitations of the LBM schemes available in the literature,
a derivation of a three-dimensional model for capturing heat transfer
phenomena across solid-fluid interfaces is proposed.
Model will be implemented to run on multi-GPU architectures allowing for
massively parallel computations.